Are supplied magnets and assemblies
compliant to RoHS?
RoHS is the abbreviation of “The Restriction of the Use of
Certain Hazardous Substance in Electrical & Electronic Equipment”. According
to European Community directive 2002/95/EC of 27th January 2003, the content of
hazardous material of Pb, Cd, Hg, Cr6+, PBDEs and PBBs in all parts should be
controlled within specified PPM. This directive was launched from 1st July 2006.
All our magnets and magnetic assemblies have been convinced conforming to EU
directive 2002/95/EC by SGS or other recognized third party.
How to make a magnet output maximum
holding force?
Different magnetization pattern and forming magnet with pole
pieces can output various holding force even if magnet with same dimension and
at same property. Below figures offer reference on design a component for
holding application.
 |
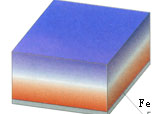 |
Holding Factor
1
magnetised through thickness |
Holding Factor
1.3
magnetised through thickness with iron backing plate |
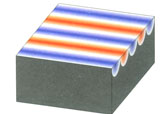 |
 |
Holding Factor
3
alternate poles on one surface |
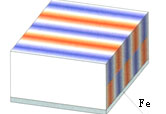
Holding Factor 3.5
magnetised through thickness ,But with iron backing
plate |
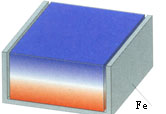 |
 |
Holding Factor 5.8
magnetised through thickness
but in iron U-shape |
Holding Factor 18
magnetised through thickness ,but with two iron pole pieces |
The above mentioned holding factors base consideration of
anistropic hard ferrite magnet. Besides above examples, there are many other
variants for certain applications. The indicated values are approximate one and
depend on the strength of the iron backing plates, and on the volume of the
magnet as well as on the structure of the magnet system.
What should be considered in designing
permanent magnet?
Basic problems of permanent magnet design revolve around
estimating the distribution of magnetic flux in a magnetic circuit, which may
include permanent magnets air gaps, high permeability condition elements and
electrical currents. Exact solutions of magnet design require complex and
comprehensive analysis of many factors. From the view of a permanent magnet
supplier, below factors on magnet should be considered.
1) Magnet material type (covering magnetic, physical and
mechanical
?
properties)
2) Magnetization pattern
3) Geometry
4)
Dimension and tolerance
5) Coating type
6) Cost
7) Working environment
8) Assembling process
9) Special requirement
It is not always possible to maximize all requirements at the
same time. Below table offers brief comparison on different type permanent
magnet and is intended to be beneficial to your design.
Material Type |
(BH)max
( kJ/m3 ) |
Tw( ? ) |
Tc( ? ) |
?(Br)
( %/? ) |
Anti Corrosion |
Cost |
Sintered Ferrite |
8.0-36.0 |
-40 to 250 |
450 |
-0.200 to -0.180 |
Excellent |
Cheap |
Bonded Ferrite |
2.0-17.6 |
-40 to 200 |
450 |
-0.200 to -0.180 |
Excellent |
Cheap |
Sintered NdFeB |
220-448 |
<80-230 |
310-350 |
-0.130 to -0.090 |
Poor |
Expensive |
Bonded NdFeB |
8.0-96.0 |
<120-180 |
310-350 |
-0.160 to -0.070 |
Fair |
Fair |
AlNiCo |
9.0-88.0 |
<450-550 |
760-860 |
-0.030 to -0.014 |
Excellent |
Fair |
Sintered SmCo |
110-264 |
<250-350 |
750-800 |
-0.050 to -0.010 |
Excellent |
Expensive |
What degree of homogeneity of
property, surface gauss and flux we can keep?
Both highest property and homogeneity are goals we have been
struggling for and will stick at. Magnetic property homogeneity means property
deviation range between the same lot products or between different production
lots. It is a systematic engineering to keep homogeneities of property, surface
gauss and flux. Besides material composition, powder particle size and processes
of molding, sintering, machining process and coating also determine
homogeneities of magnetic property, surface gauss and flux.
In powder making process, we control the powder particle size
to keep homogenous magnetic property; in molding process, we stabilize the
molding force pressure and change manual material-feeding with automatic
material-feeding to get uniform density of semi-product; in sintering process,
we stabilize sintering temperature and change coal heating furnace with
electric-power furnace in sintering hard ferrite magnet to get homogenous
magnetic property; in machining process, we control the deviations of dimension
and angle between geometric axial and anisotropic axial to improve homogeneity
of magnet dimension, dimension ratio and pole deviation; in coating process, we
control coating layer thickness (determining air gap), and time and
concentration of acid in washing magnet to enhance homogeneity of dimension and
dimension ratio.
These actions are doubtlessly helpful to fulfill our goals.
For information on values of homogeneity, please contact us.
What is called angle of
orientation/anisotropy direction of the magnet?
In fact it is called the angle of orientation/anisotropic
direction and geometric axis of magnet. For particular applications, customer
requires conformity of the two axes or orientation/anisotropy direction and a
machined slot. Limited by process technology, absolute conformity of axes is
impossible. It happens on molding, sintering and machining processes. The job we
can do is to utmostly reduce the angle of the axes. Our talent partner has
accumulate rich experience on controlling the angle and found a scientific way
to measure the angle.
What is called “Quality Coefficient K”
on hard ferrite magnet?
Quality Coefficient K is a data to evaluate quality and grade
of raw material of ferrite magnet. The calculation of K value follows below
equation:
K=Br+0.4iHc??(Br in unit of mT, iHc
in unit of kA/m)
In sintering process, increasing temperature by per 10? can
promote remanence Br by 5mT and meanwhile decrease intrinsic coercive force by
12kA/m. If the used material is qualified, then the K value is a constant one in
spite of temperature change. Magnet with higher K value is with capability of
outputting higher remeance Br and intrinsic coercive force.
What items should be negotiated before
purchasing a magnet and included in an inquiry?
The below checklist maybe helpful in constructing and
communicating specifications for permanent magnet:
1) Material type
2) Typical, Minimum and / or maximum magnetic properties (Br,
Hc, iHc, (BH)max)
3) Geometry
4) Dimension and tolerance
5) Orientation direction (and tolerance of orientation
direction if critical)
6) Magnetizing status
7) Coating
8) Acceptance test or performance requirements
9) Inspection sampling plan
10) Packing and identification
11) Other requirement.
Why there are some crystal/shinning
points on the surface of sintered ferrite magnet?
If the sintering temperature is approaching the upper limit of
the designed temperature of the used material, then some crystal/shinning points
will appear on the surface of sintered ferrite magnet. Magnet with this
phenomenon does not influence its function. Generally, such kind of magnet is
with higher remanence Br and lower intrinsic coercive force iHc but within the
property range.
Why measuring surface gauss by gauss
meter to express flux density is not scientific?
Flux density expresses the concentration of line of force per
unit area passing from one pole to the other. Magnet material type, dimension
ratio and air gap determines the measured flux density.
In measuring surface gauss, the position change of hall probe
sensitively influence the reading result. Placing probe at the magnet edge area
can get much higher value than by placing hall probe at the central area of
magnet. Due to technology problem, the reading on “N” pole and “S” will be quite
different particularly the measured magnet is an anisotropic axially magnetized
hard ferrite magnet. Sometimes, the surface gauss difference between 2 poles
will be over 100Gs.
|



